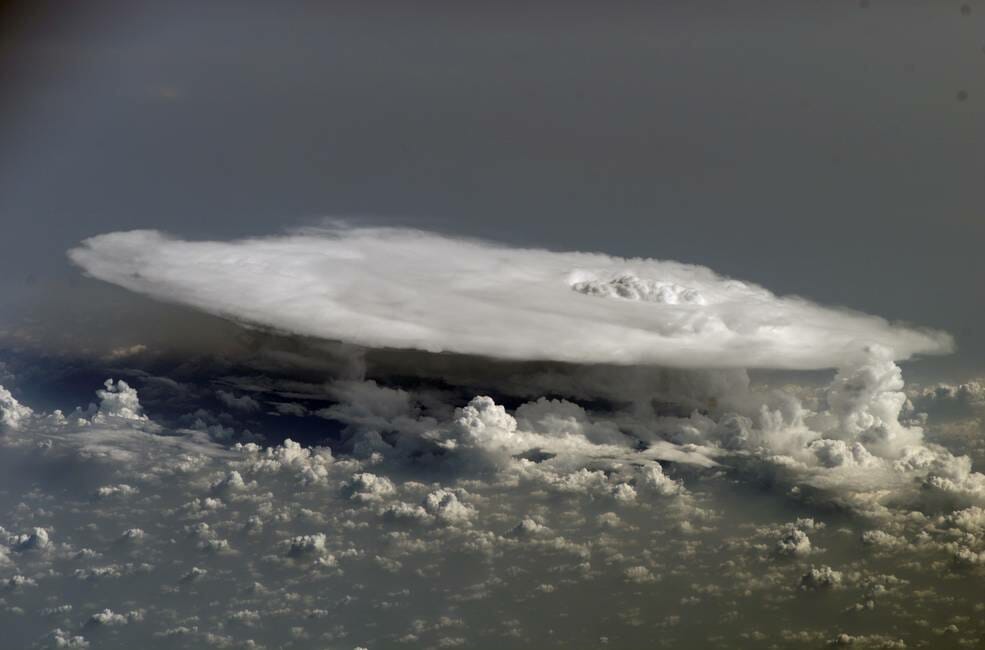
NASA‘s selection of the PolSIR mission marks an important step in understanding Earth’s atmosphere, particularly the behavior of ice clouds found at high altitudes in tropical and sub-tropical regions. Ice clouds play a significant role in the global climate system, and studying them in detail is crucial for improving climate forecasts and simulations.
The PolSIR mission will utilize two CubeSats, small satellites measuring just over a foot tall, placed in separate orbits with a time difference of three to nine hours. This configuration will allow the instruments to observe the daily cycle of ice content within the clouds over an extended period.
By focusing on ice clouds, the PolSIR mission aims to provide valuable insights into their response to a changing climate and their contribution to further atmospheric changes. Understanding these dynamics is a significant challenge in predicting the future behavior of Earth’s atmosphere.
With a total budget of no more than $37 million for the mission’s lifecycle costs, excluding launch expenses, the PolSIR instrument falls under the Earth Venture program. Earth Venture instruments are designed to have targeted research goals while keeping costs relatively low. These instruments often hitch a ride on other missions or commercial satellites to minimize launch costs and provide frequent flight opportunities.
The radiometers used in the PolSIR mission will measure the radiant energy emitted by ice clouds, greatly enhancing our understanding of their daily changes and responses. The data collected will contribute to improving climate models and our overall comprehension of the Earth system.
The mission’s principal investigator is Ralf Bennartz from Vanderbilt University, while Dong Wu from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center serves as the deputy principal investigator. NASA Goddard will manage the project and oversee the construction of the two instruments. Science operations will be conducted by the Space Science and Engineering Center at the University of Wisconsin – Madison. The spacecraft themselves will be built by Blue Canyon Technologies in Lafayette, Colorado.
The PolSIR mission represents NASA’s ongoing commitment to studying Earth and its climate system, selecting missions that provide targeted research opportunities and contribute to our understanding of the factors driving global change. By investigating ice clouds with unprecedented detail, this mission will advance our knowledge and help refine climate predictions for the benefit of society and the planet.